Abstract
Perspective
Dendritic cells and TNF-Related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) represent new possibilities for sepsis treatment
Petya Ganova, Lyudmila Belenska-Todorova and Nina Ivanovska*
Published: 14 November, 2017 | Volume 1 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-004
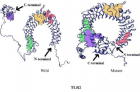
Sepsis refers to a generalized inflammatory response of the organism to an infection or to bacterial products in circulation, rather than the development of an infection per se. Despite recent advances in clinical practice and overall medical care, sepsis remains a great health care problem and is still the most common cause of death in critically ill patients with infection. We suppose that during the course of sepsis the expression of TRAIL in different organs correlates with acute mortality and further development of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). It is expected that dendritic cells (DCs) might become targets for apoptotic processes in a result of elevated TRAIL expression. This hypothesis is a bias for detailed investigations for in vivo studies in animal models and for in vitro studies of septic patients.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.hcci.1001001 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- Aziz M, Jacob A, Yang WL, Matsuda A, Wang P. Current trends in inflammatory and immunomodulatory mediators in sepsis. J Leukoc Biol. 2013; 93: 329-342. Ref.: https://goo.gl/T8Lre4
- Deutschman CS, Tracey KJ. Sepsis: current dogma and new perspectives. Immunity. 2014; 40: 463-475. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ykFSX8
- Bozza FA, Salluh JI, Japiassu AM, Marcio Soares, Edson F Assis,et al. Cytokine profiles as markers of disease severity in sepsis: a multiplex analysis. Crit Care. 2007; 11: 49. Ref.: https://goo.gl/zWRgqj
- Dinarello CA. Historical insights into cytokines. Eur J Immunol. 2007; 37: 34-45. Ref.: https://goo.gl/HVWTvG
- Russell JA. Management of sepsis. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355: 1699-1713. Ref.: https://goo.gl/fs8BRF
- Teijaro JR. Cytokine storms in infectious diseases. Semin Immunopathol. 2017; 39: 501-503. Ref.: https://goo.gl/PsGGJS
- van der Poll T, van de Veerdonk FL, Scicluna BP, Netea MG. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017; 17: 407-420. Ref.: https://goo.gl/18HR7r
- Wiersinga WJ, Leopold SJ, Cranendonk DR, van der Poll T. Host innate immune responses to sepsis. Virulence. 2014; 5: 36-44. Ref.: https://goo.gl/CfL6Yy
- Tse MT. Trial watch: Sepsis study failure highlights need for trial design rethink. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013; 12: 334. Ref.: https://goo.gl/5z82Lp
- Flohé SB1, Agrawal H, Schmitz D, Gertz M, Flohé S,et al. Dendritic cells during polymicrobial sepsis rapidly mature but fail to initiate a protective Th1-type immune response. J Leukoc Biol. 2006; 79: 473-481. Ref.: https://goo.gl/JWXsZX
- Wu DD, Li T, Ji XY. Dendritic Cells in Sepsis: Pathological Alterations and Therapeutic Implications. J Immunol Res. 2017. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Ya1BYB
- de Aguiar BB, Girardi I, Paskulin DD, de Franca E, Dornelles C,et al. CD14 expression in the first 24h of sepsis: effect of -260C>T CD14 SNP. Immunol Invest. 2008; 37: 752-769. Ref.: https://goo.gl/CT56x1
- Reinhart K1, Glück T, Ligtenberg J, Tschaikowsky K, Bruining A,et al. CD14 receptor occupancy in severe sepsis: results of a phase I clinical trial with a recombinant chimeric CD14 monoclonal antibody (IC14). Crit Care Med. 2004; 32: 1100-1108. Ref.: https://goo.gl/uiQswv
- Schaaf B1, Luitjens K, Goldmann T, van Bremen T, Sayk F, et al. Mortality in human sepsis is associated with downregulation of Toll-like receptor 2 and CD14 expression on blood monocytes. Diagn Pathol. 2009 ;4: 12. Ref.: https://goo.gl/isro1J
- Cristofaro P, Opal SM. The Toll-like receptors and their role in septic shock. Expert Opin Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2003; 7: 603-612. Ref.: https://goo.gl/NpxSmk
- Chaudhry H, Zhou J, Zhong Y, Ali MM, McGuire F, et al. Role of cytokines as a double-edged sword in sepsis. In Vivo. 2013; 27: 669-684. Ref.: https://goo.gl/NDQzoU
- Gogos CA, Drosou E, Bassaris HP, Skoutelis A. Pro- versus anti-inflammatory cytokine profile in patients with severe sepsis: a marker for prognosis and future therapeutic options. J Infect Dis. 2000; 181: 176-180. Ref.: https://goo.gl/4roqgz
- Wen H, Hogaboam CM, Gauldie J, Kunkel SL, et al. Severe sepsis exacerbates cell-mediated immunity in the lung due to an altered dendritic cell cytokine profile. Am J Pathol. 2006; 168: 1940-1950. Ref.: https://goo.gl/V9mktc
- Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW, Swanson PE, Grayson MH, Osborne DF, et al. Depletion of dendritic cells, but not macrophages, in patients with sepsis. J Immunol. 2002; 168: 2493-2500. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Gna8r2
- Mera S, Tatulescu D, Cismaru C, Bondor C, Slavcovici A, et al. Multiplex cytokine profiling in patients with sepsis. APMIS. 2011; 119: 155-163. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VxmKoi
- Efron PA, Martins A, Minnich D, Tinsley K, Ungaro R,et al. Characterization of the systemic loss of dendritic cells in murine lymph nodes during polymicrobial sepsis. J Immunol. 2004; 173: 3035-3043. Ref.: https://goo.gl/orCkgy
- Strother RK, Danahy DB, Kotov DI, Kucaba TA, Zacharias ZR, et al. Polymicrobial Sepsis Diminishes Dendritic Cell Numbers and Function Directly Contributing to Impaired Primary CD8 T Cell Responses In Vivo. J Immunol. 2016; 197: 4301-4311. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Aid1YL
- Tinsley KW, Grayson MH, Swanson PE, Drewry AM, Chang KC,et al. Sepsis induces apoptosis and profound depletion of splenic interdigitating and follicular dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2003; 171: 909-914. Ref.: https://goo.gl/5FpcHr
- Boomer JS, To K, Chang KC, Takasu O, Osborne DF, et al. Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis and multiple organ failure. JAMA. 2011; 306: 2594-2605. Ref.: https://goo.gl/N8hZjs
- Fattahi F, Ward PA. Understanding Immunosuppression after Sepsis. Immunity. 2017; 47: 3-5. Ref.: https://goo.gl/vWQAGP
- Wesche DE, Lomas-Neira JL, Perl M, Chung CS, Ayala A. Leukocyte apoptosis and its significance in sepsis and shock. J Leukoc Biol. 2005; 78: 325-337. Ref.: https://goo.gl/jPBA1S
- Bayir H, Kagan VE. Bench-to-bedside review: Mitochondrial injury, oxidative stress and apoptosis--there is nothing more practical than a good theory. Crit Care. 2008; 12: 206. Ref.: https://goo.gl/YHgvrb
- Schneider P, Olson D, Tardivel A, Browning B, Lugovskoy A, et al. Identification of a new murine tumor necrosis factor receptor locus that contains two novel murine receptors for tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). J Biol Chem. 2003; 278: 5444-5454. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ommdrh
- Daniels RA, Turley H, Kimberley FC, Liu XS, Mongkolsapaya J, et al. Expression of TRAIL and TRAIL receptors in normal and malignant tissues. Cell Res. 2005; 15: 430-438. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FFijMj
- Delano MJ, Ward PA. Sepsis-induced immune dysfunction: can immune therapies reduce mortality? J Clin Invest. 2016; 126: 23-31. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ks4Bmc
- Hotchkiss RS, Monneret G, Payen D. Immunosuppression in sepsis: a novel understanding of the disorder and a new therapeutic approach. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013; 13: 260-268. Ref.: https://goo.gl/EwjWsC
Similar Articles
-
Dendritic cells and TNF-Related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) represent new possibilities for sepsis treatmentPetya Ganova,Lyudmila Belenska-Todorova,Nina Ivanovska*. Dendritic cells and TNF-Related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) represent new possibilities for sepsis treatment. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hcci.1001001; 1: 001-004
-
Brain response in some systemic immune condition-Toxicological aspectsLuisetto M*. Brain response in some systemic immune condition-Toxicological aspects. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001002; 1: 005-008
-
The Immunitary role in chronic prostatitis and growth factors as promoter of BPHMauro luisetto*,Behzad Nili-Ahmadabadi,Ghulam Rasool Mashori,Ram Kumar Sahu,Farhan Ahmad Khan,Cabianca luca,Heba Nasser. The Immunitary role in chronic prostatitis and growth factors as promoter of BPH. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001003; 2: 001-013
-
Expression of C-type Natriuretic Peptide and its Specific Guanylyl Cyclase-Coupled Receptor in Pig Ovarian Granulosa CellsSoo Mi Kim,Suhn Hee Kim,Kyung Woo Cho,Sun Young Kim,Sung Zoo Kim*. Expression of C-type Natriuretic Peptide and its Specific Guanylyl Cyclase-Coupled Receptor in Pig Ovarian Granulosa Cells. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001004; 2: 014-025
-
Endogenous Ligands of Toll Like Receptors: A Danger Signal to the Brain Memory at High AltitudeKP Mishra*,Shashi Bala Singh. Endogenous Ligands of Toll Like Receptors: A Danger Signal to the Brain Memory at High Altitude. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001005; 2: 026-027
-
Differentiation of bone marrow cells in arthritic mice with decreased complement activityPetya Ganova,Nina Ivanovska*. Differentiation of bone marrow cells in arthritic mice with decreased complement activity. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001006; 2: 028-038
-
Effect of common food additives on mast cell activationCarena MP,Mariani ML,Ordóñez A,Penissi AB*. Effect of common food additives on mast cell activation. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001007; 3: 001-005
-
Association of Toll-like receptor 2, 4, and 9 gene polymorphism with high altitude induced thrombosis patients in Indian populationSwati Sharma,Iti Garg*,Gauri Mishra,Babita Kumari,Lilly Ganju,Bhuvnesh Kumar. Association of Toll-like receptor 2, 4, and 9 gene polymorphism with high altitude induced thrombosis patients in Indian population. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001008; 3: 006-015
-
Altitude sickness and Antarctic polar plateau: A reviewKP Mishra*,Shashi Bala Singh. Altitude sickness and Antarctic polar plateau: A review. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001009; 3: 016-018
-
Proposal for the elimination of allergiesJames F Walles*. Proposal for the elimination of allergies. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.icci.1001010; 3: 019-019
Recently Viewed
-
Transumbilical Single-incision Hiatal Hernia Repair and Nissen Fundoplication in situs Inversus Totalis: A Rare Case ReportQing Cao,Chen Kang,Kang Gu,Yin Peng,Yang Lv,Xu-Zhong Ding,Peng Li*. Transumbilical Single-incision Hiatal Hernia Repair and Nissen Fundoplication in situs Inversus Totalis: A Rare Case Report. Adv Treat ENT Disord. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.ated.1001017; 10: 001-003
-
NAD⁺ Biology in Ageing and Chronic Disease: Mechanisms and Evidence across Skin, Fertility, Osteoarthritis, Hearing and Vision Loss, Gut Health, Cardiovascular–Hepatic Metabolism, Neurological Disorders, and MuscleRizwan Uppal,Umar Saeed*,Muhammad Rehan Uppal. NAD⁺ Biology in Ageing and Chronic Disease: Mechanisms and Evidence across Skin, Fertility, Osteoarthritis, Hearing and Vision Loss, Gut Health, Cardiovascular–Hepatic Metabolism, Neurological Disorders, and Muscle. Ann Clin Endocrinol Metabol. 2026: doi: 10.29328/journal.acem.1001032; 10: 001-009
-
Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical TrialAnders Wänman*, Susanna Marklund, Negin Yekkalam. Treatment Outcome in Patients with Myofascial Orofacial Pain: A Randomized Clinical Trial. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001046; 9: 001-008
-
Anxiety and depression as an effect of birth order or being an only child: Results of an internet survey in Poland and GermanyJochen Hardt*,Lisa Weyer,Malgorzata Dragan,Wilfried Laubach. Anxiety and depression as an effect of birth order or being an only child: Results of an internet survey in Poland and Germany. Insights Depress Anxiety. 2017: doi: 10.29328/journal.hda.1001003; 1: 015-022
-
Case Report of a Child with Beta Thalassemia Major in a Tribal Region of IndiaNeha Chauhan, Prakash Narayan, Mahesh Narayan, Manisha Shukla*. Case Report of a Child with Beta Thalassemia Major in a Tribal Region of India. J Child Adult Vaccines Immunol. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcavi.1001011; 7: 005-007
Most Viewed
-
Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization)Dasse Sery Romuald*, KL Siransy, N Koffi, RO Yeboah, EK Nguessan, HA Adou, VP Goran-Kouacou, AU Assi, JY Seri, S Moussa, D Oura, CL Memel, H Koya, E Atoukoula. Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization). Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001035; 8: 007-012
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037
-
Snow white: an allergic girl?Oreste Vittore Brenna*. Snow white: an allergic girl?. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001029; 6: 001-002
-
Cytokine intoxication as a model of cell apoptosis and predict of schizophrenia - like affective disordersElena Viktorovna Drozdova*. Cytokine intoxication as a model of cell apoptosis and predict of schizophrenia - like affective disorders. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001028; 5: 038-040

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."